
Cognitive structures are patterns of physical or mental action that underlie specific acts of intelligence and correspond to stages of child development (see Schemas). The concept of cognitive structure is central to his theory. Piaget had a background in both Biology and Philosophy and concepts from both these disciplines influences his theories and research of child development.
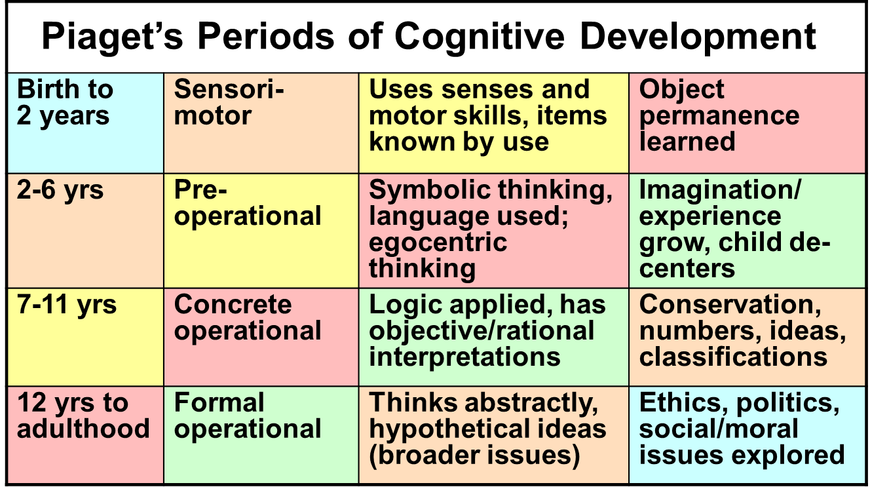
Piaget called his general theoretical framework “genetic epistemology” because he was primarily interested in how knowledge developed in human organisms.

Over a period of six decades, Jean Piaget conducted a program of naturalistic research that has profoundly affected our understanding of child development.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
